What Are Research Peptides and How Do They Work?
In the realm of modern scientific advancements, research peptides have emerged as powerful tools for understanding biological processes, exploring new therapies, and unlocking the mysteries of human health. But what exactly are research peptides, and how do they work? This article provides a comprehensive overview of research peptides, their functions, and their potential in laboratory studies.
What Are Research Peptides?
Peptides are short chains of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, that play essential roles in various physiological functions. Research peptides are synthetic or naturally derived sequences of amino acids specifically designed for scientific studies. These peptides mimic the structure and function of natural peptides found in the body, enabling researchers to investigate their effects in controlled environments.
Key Characteristics of Research Peptides:
- Comprised of 2 to 50 amino acids.
- Serve as signaling molecules that regulate biological functions.
- Synthesized with high purity for experimental precision.
Research peptides are widely used in fields such as molecular biology, pharmacology, and biochemistry to explore cellular communication, tissue repair, metabolic processes, and more.
How Do Research Peptides Work?
Research peptides function by interacting with specific receptors on cells or by mimicking natural biological processes. Each peptide is tailored to target particular systems or mechanisms in the body. Once introduced into a laboratory setting, peptides bind to their target sites and activate, inhibit, or regulate specific cellular pathways.
Mechanisms of Action:
- Receptor Binding: Many research peptides act as ligands, binding to cell surface receptors and triggering a cascade of biological responses.
- Mimicking Natural Peptides: Synthetic peptides replicate the behavior of naturally occurring peptides, making it easier to study processes like hormone signaling and immune modulation.
- Enzyme Modulation: Some peptides regulate enzymatic activity, influencing metabolic reactions or promoting tissue repair.
Common Research Applications of Peptides
Research peptides have diverse applications, offering valuable insights into numerous biological systems.
1. Tissue Repair and Regeneration
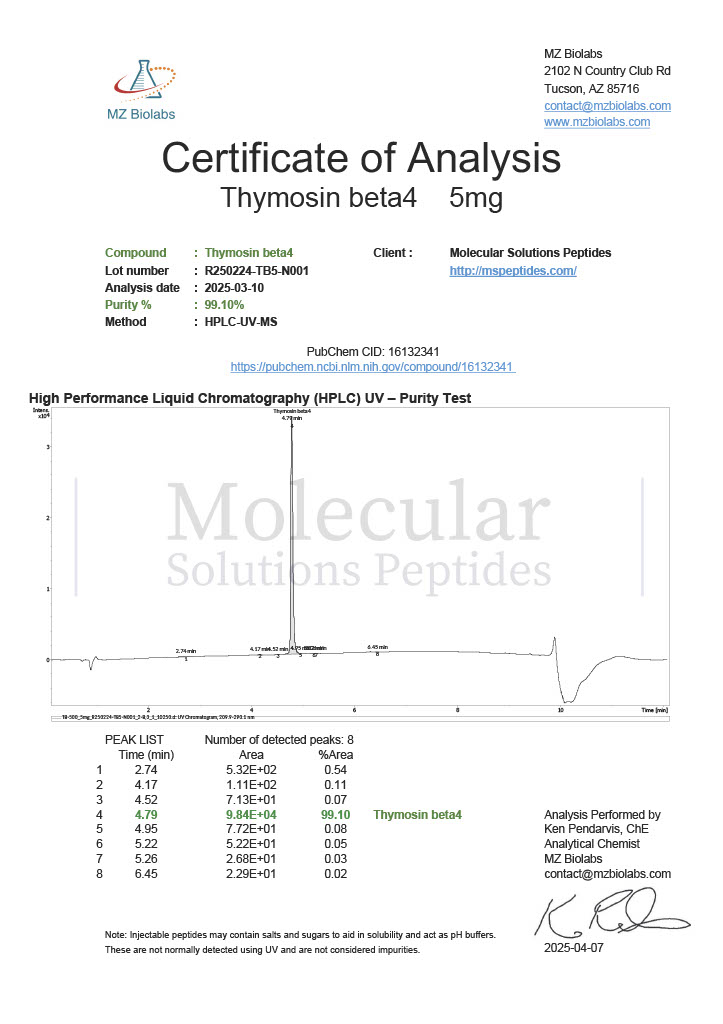
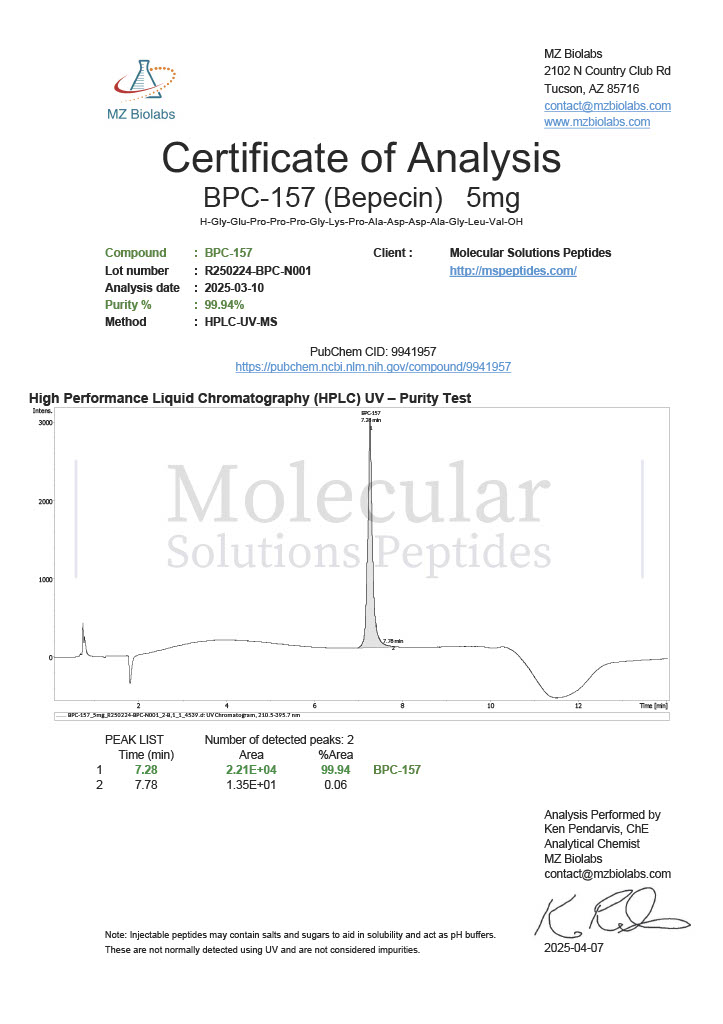
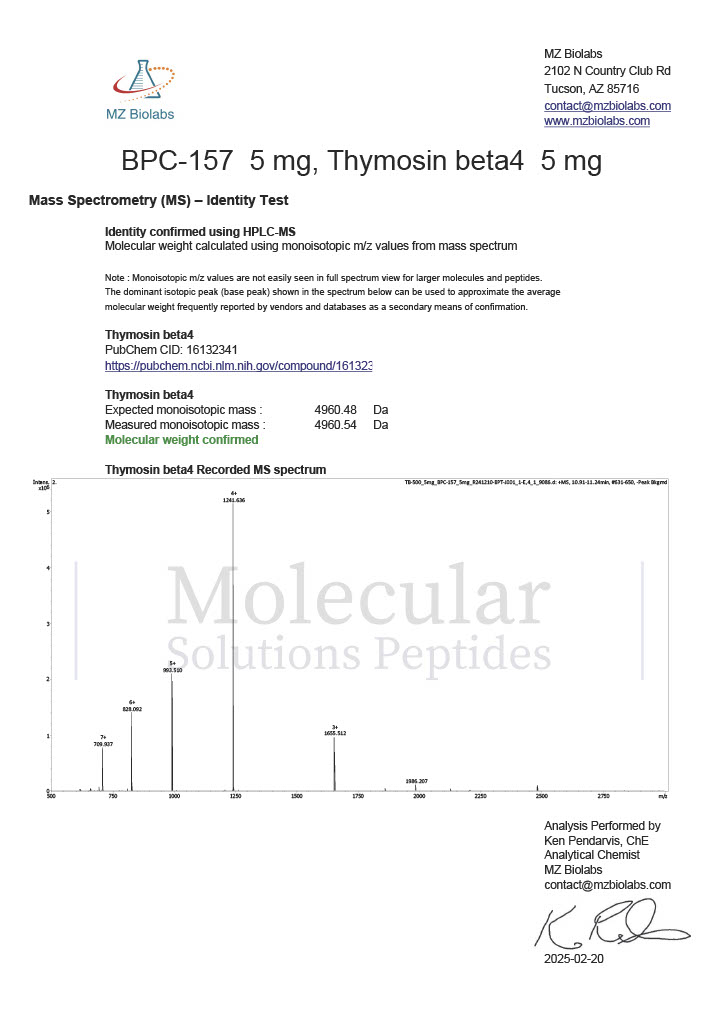
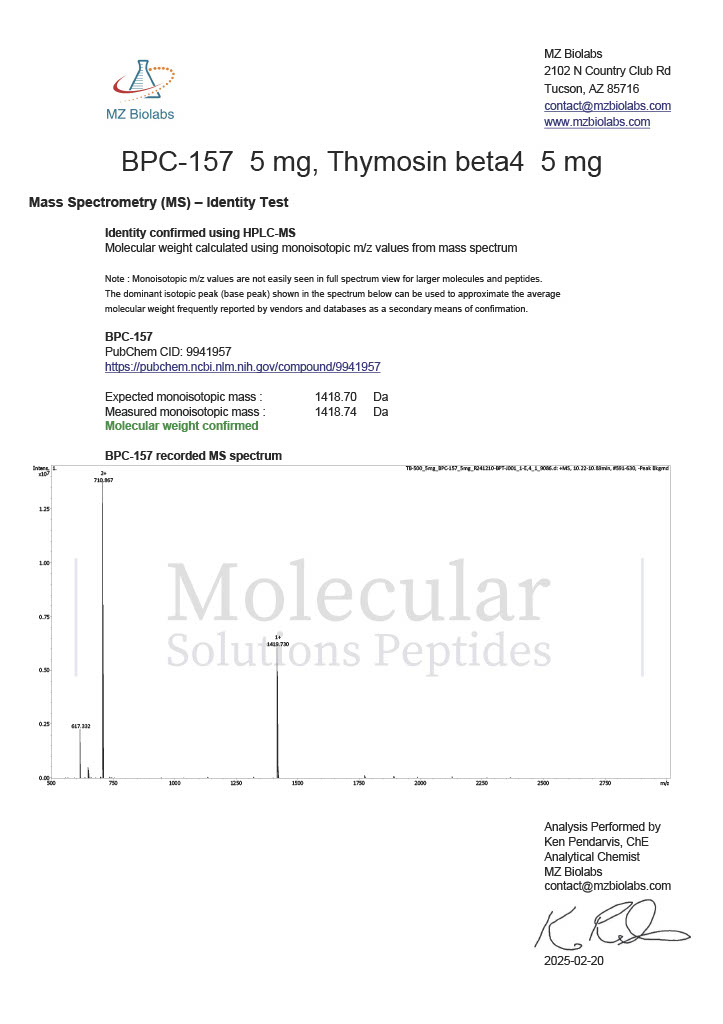
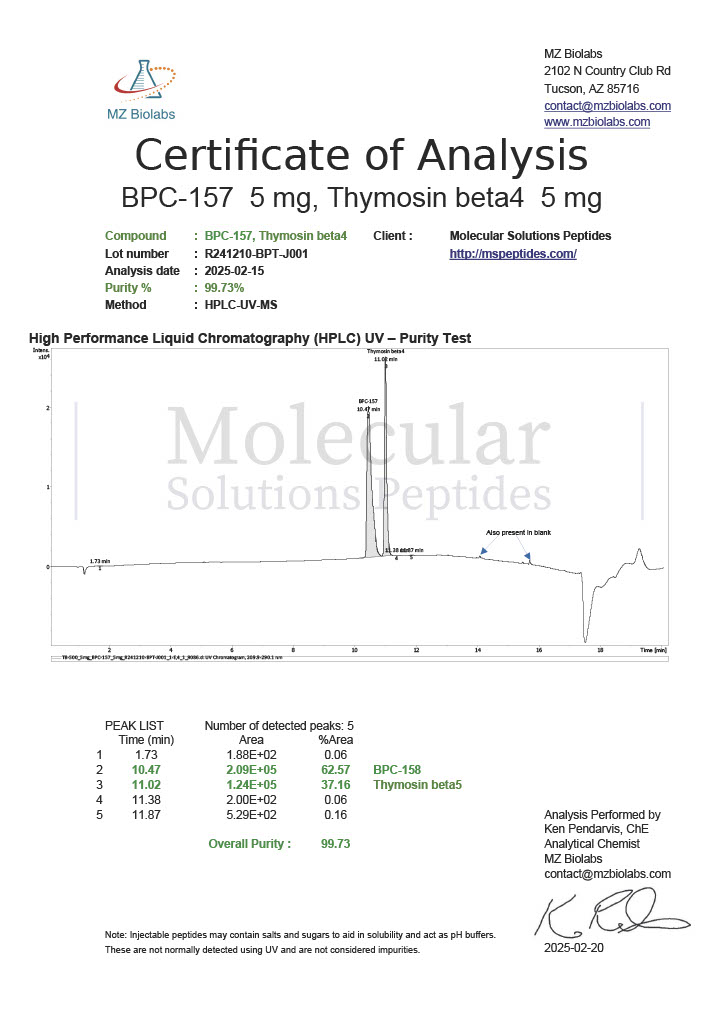
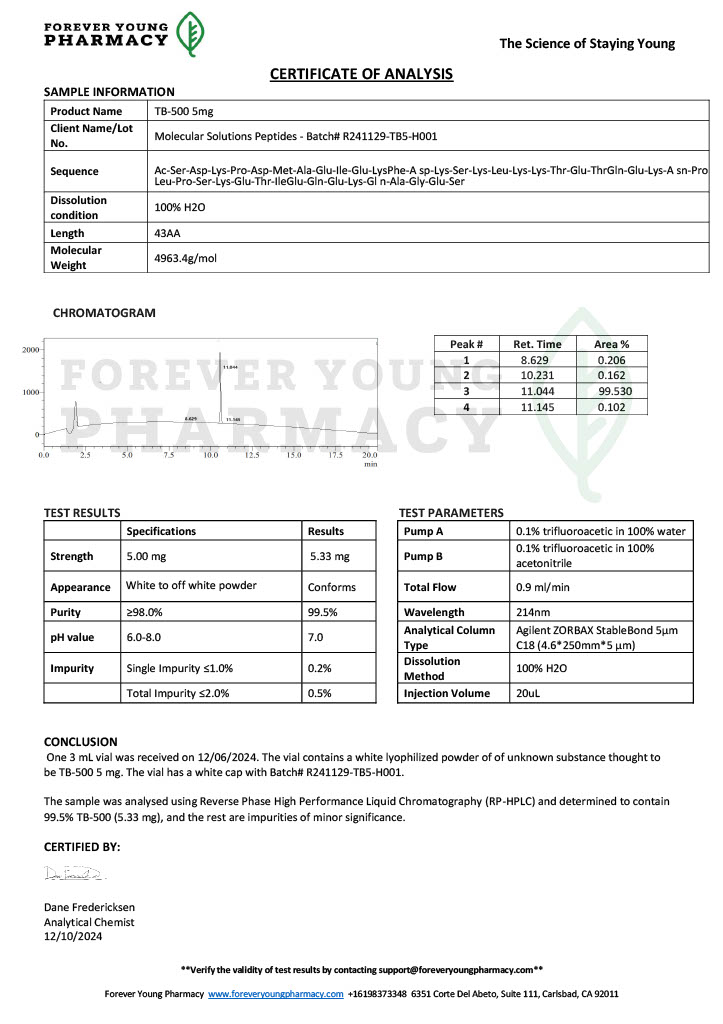
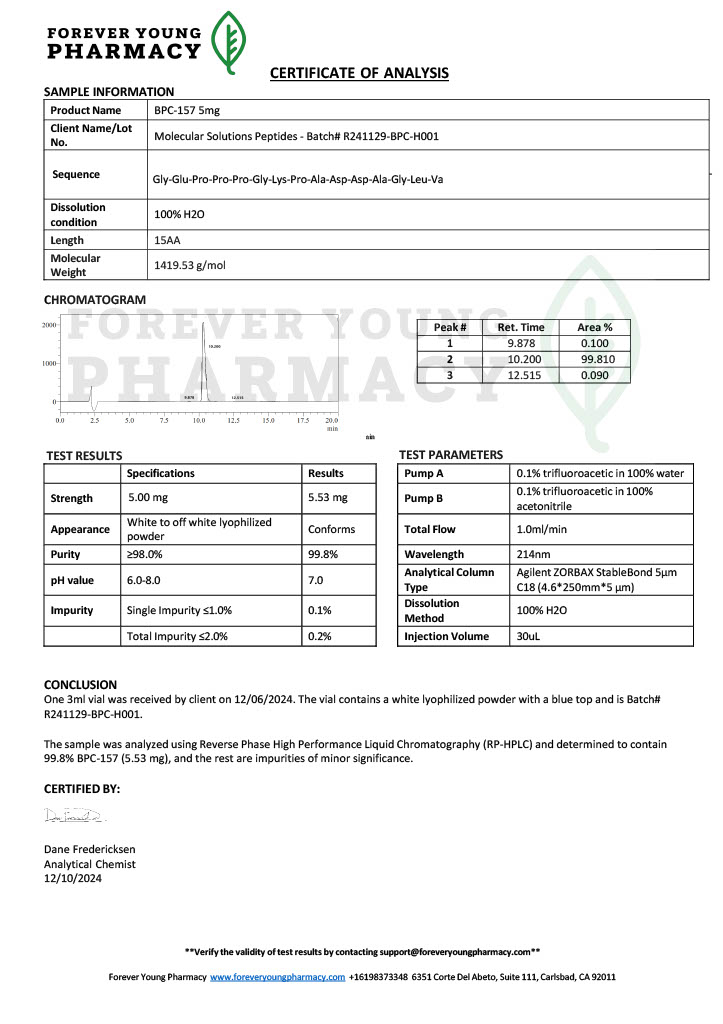
Peptides such as BPC-157 and TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4) are studied for their potential to promote wound healing, reduce inflammation, and enhance tissue repair. Their mechanisms of action often involve modulating growth factors and cell migration.
2. Metabolic and Hormonal Research
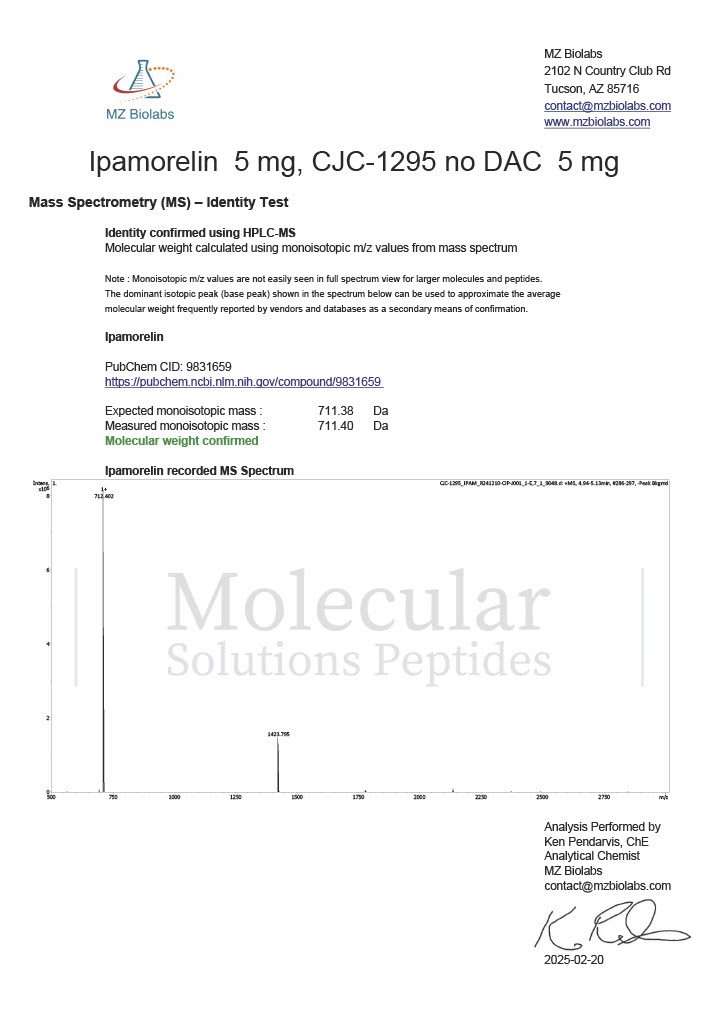
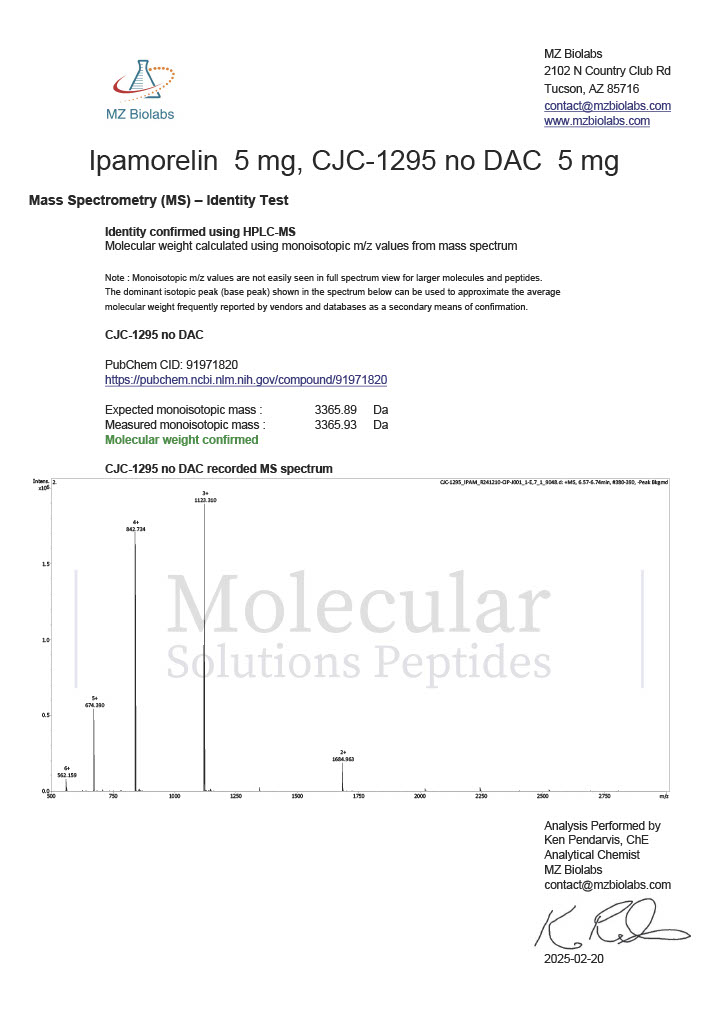
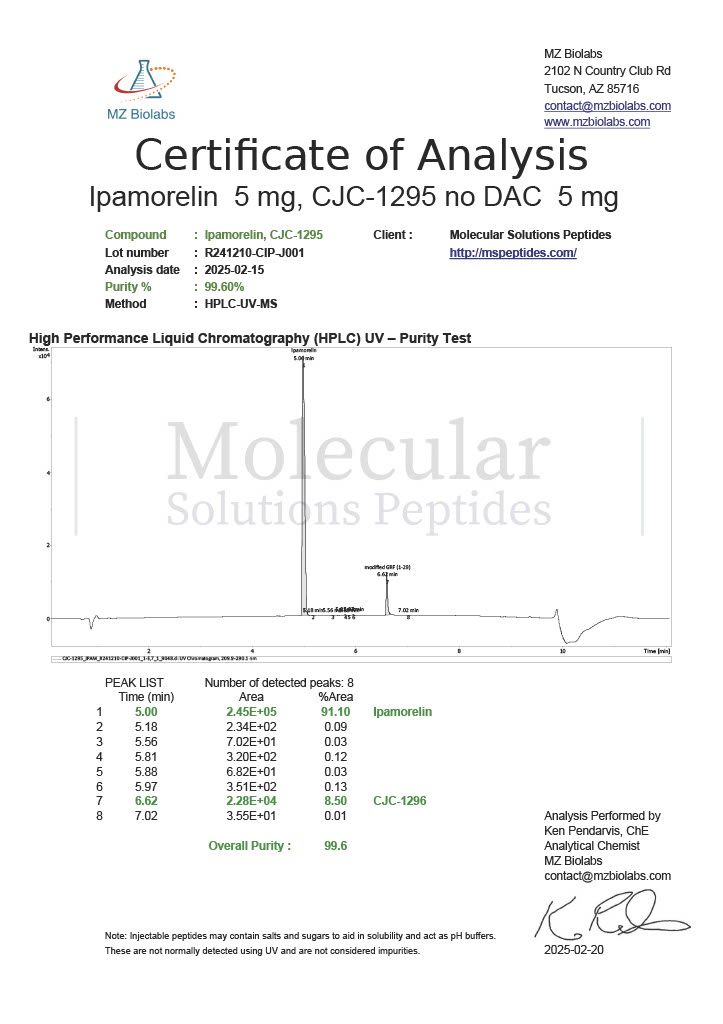
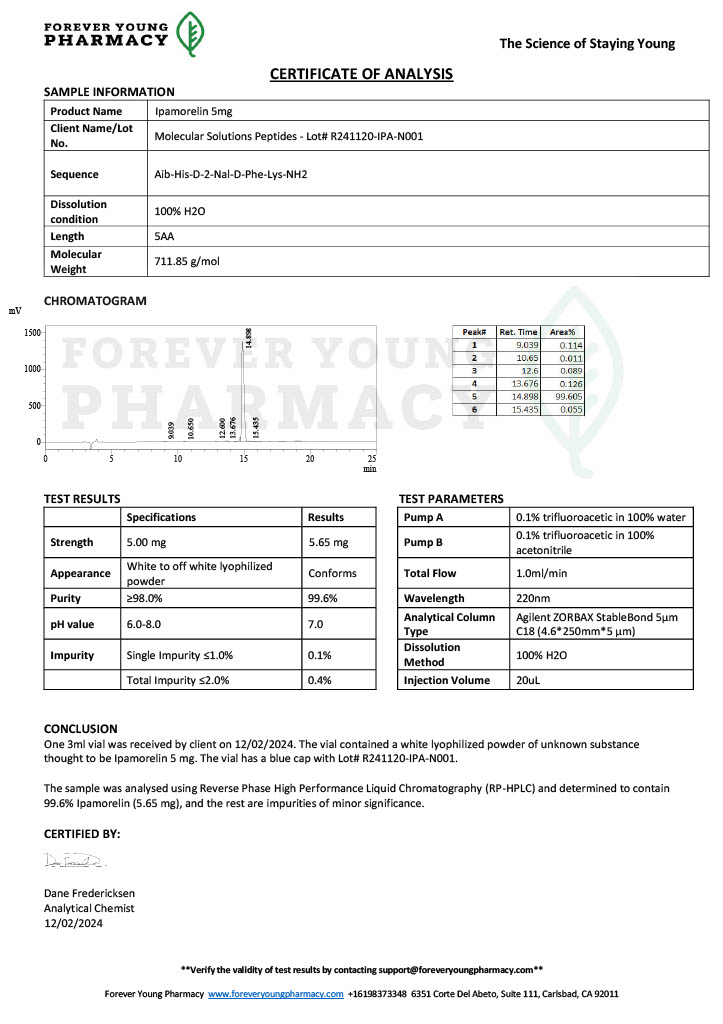
Peptides like CJC-1295 and Ipamorelin are frequently used in studies of growth hormone regulation. By stimulating the release of growth hormone, researchers explore their effects on muscle growth, fat metabolism, and recovery.
3. Weight Loss and Appetite Regulation
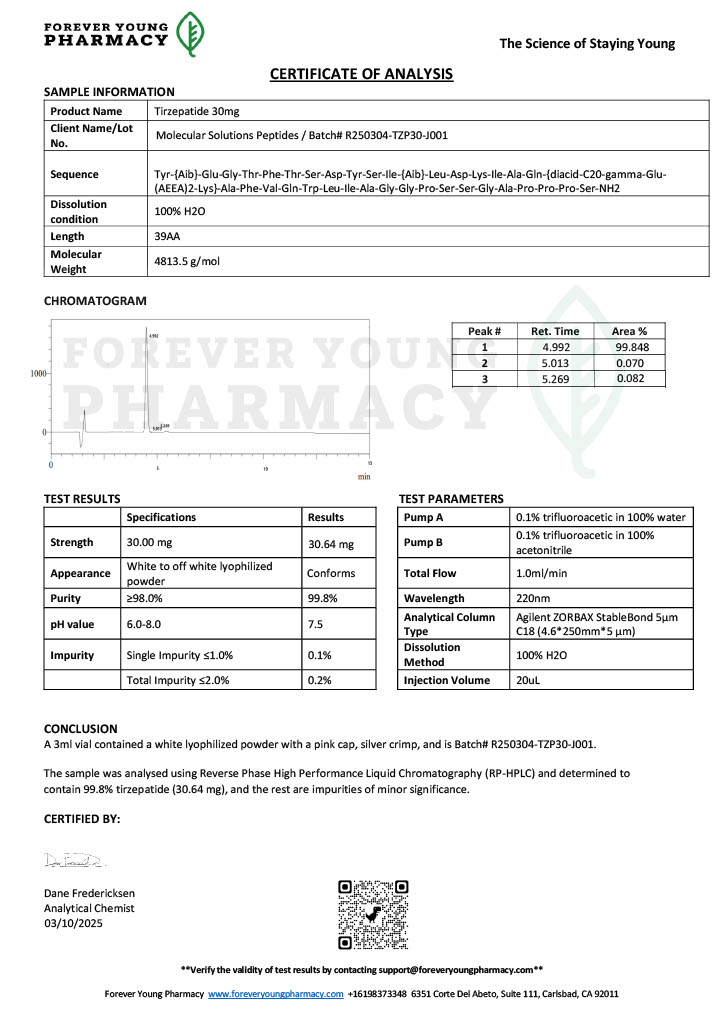
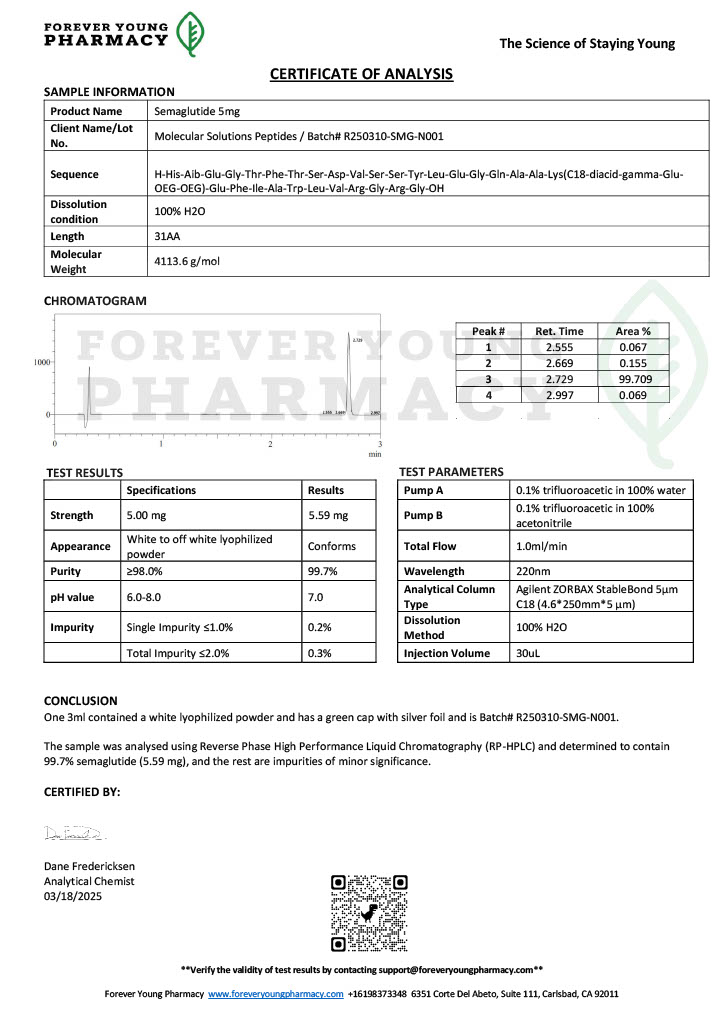
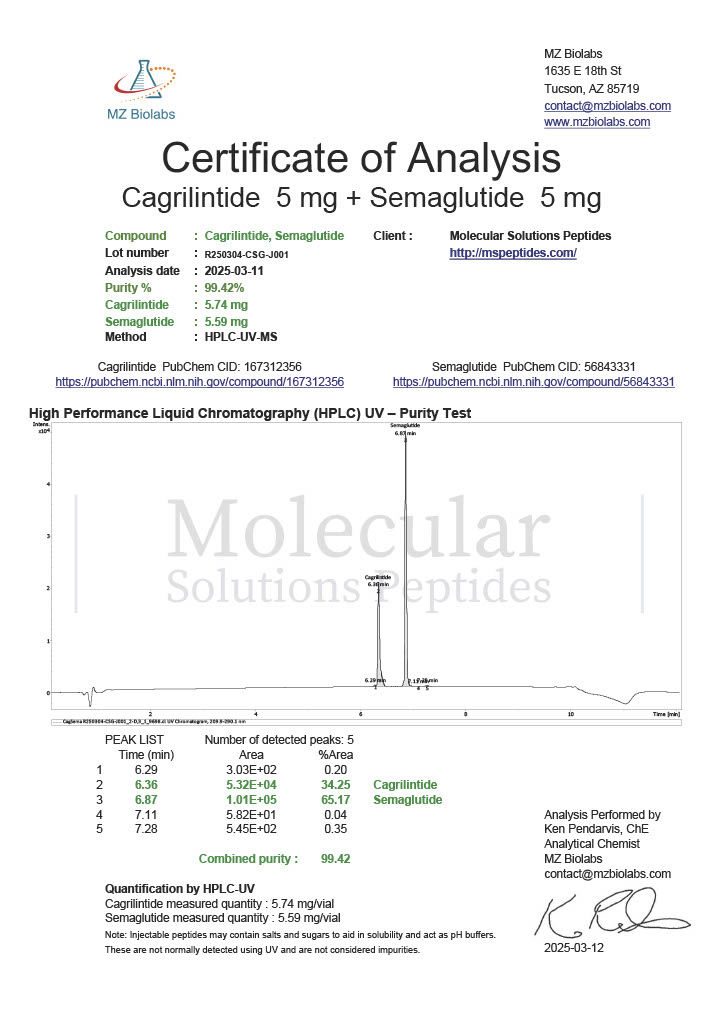
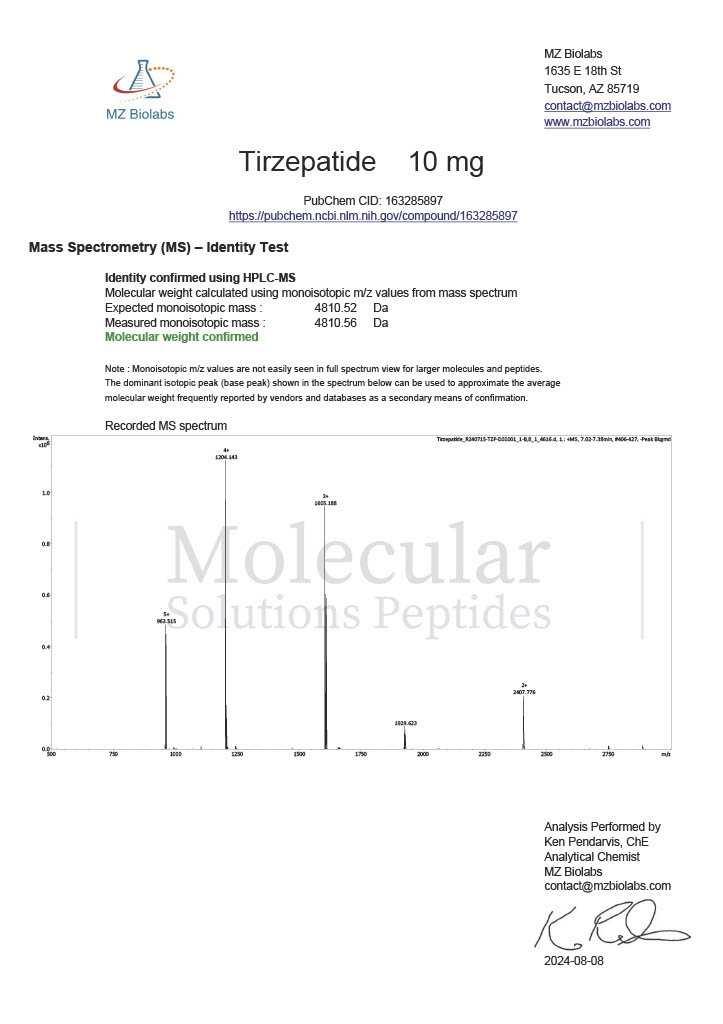
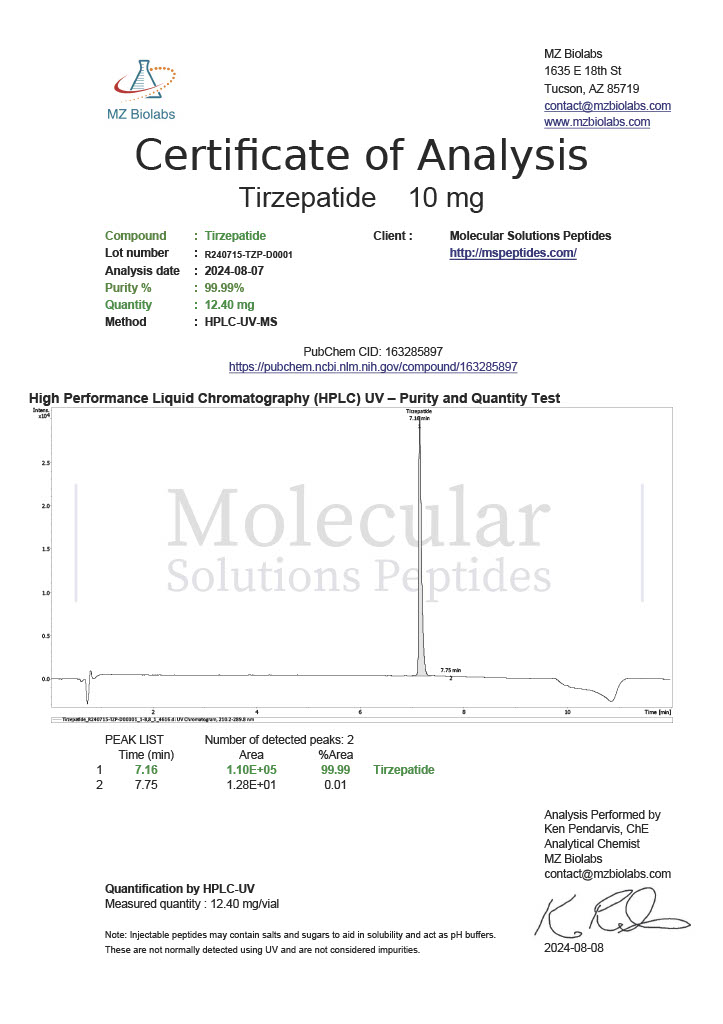
Peptides such as Semaglutide and Tirzepatide target metabolic pathways involved in glucose regulation and appetite suppression. These peptides are crucial for understanding obesity, diabetes, and related conditions.
4. Cognitive Function and Neuroprotection
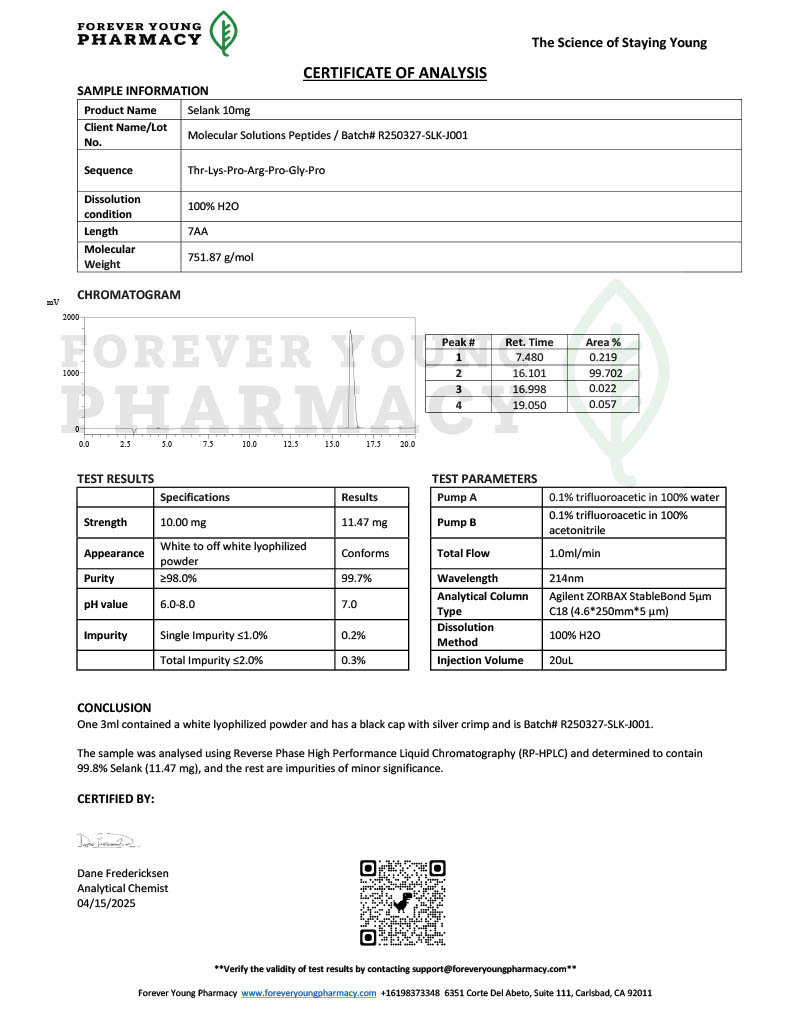
Peptides like Dihexa and Selank are being investigated for their neuroprotective properties, showing promise in enhancing memory, reducing anxiety, and protecting against cognitive decline.
5. Immune System Modulation
Certain peptides influence the immune system, either enhancing immune responses or reducing overactive inflammation. This makes them valuable tools in autoimmune and infectious disease research.
Benefits of Research Peptides
Research peptides provide a unique combination of benefits for scientists and medical researchers:
- Precision Targeting: Peptides are highly specific, allowing for targeted studies with minimal off-target effects.
- Mimicking Natural Processes: They closely replicate biological systems, making experiments more realistic and reliable.
- Therapeutic Potential: Research peptides are foundational in developing novel therapies for chronic conditions and diseases.
The Science of Research Peptides: Examples in Action
BPC-157
Known as the “body-protecting compound,” BPC-157 is studied for its effects on healing. Research has shown its potential to promote angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels), reduce inflammation, and protect against gastric damage.
CJC-1295 + Ipamorelin
These peptides are often studied together to explore their synergistic effects on growth hormone secretion. Research indicates their potential for increasing lean muscle mass, improving recovery, and supporting metabolic health.
Tirzepatide
This dual-action peptide targets both GLP-1 and GIP receptors, making it a valuable research compound for studying glucose metabolism and weight regulation in metabolic disease models.
How Are Research Peptides Used in Studies?
Research peptides are typically provided as lyophilized (freeze-dried) powders that are reconstituted with sterile solvents for laboratory use. Proper handling and storage are essential to maintain their stability and efficacy.
Usage Guidelines in Research:
- Administered in vitro (in cell cultures) or in vivo (in animal models) to study specific biological effects.
- Designed for controlled experiments under strict laboratory conditions.
- Often paired with advanced analytical techniques to measure their impact on cellular pathways.
Note: Research peptides are not approved for human consumption or therapeutic use. They are strictly for laboratory and scientific studies.
Are Research Peptides Safe?
When used in scientific research, peptides are produced under strict quality control guidelines to ensure purity and reliability. However, since research peptides are experimental, their safety profiles are still under investigation. For this reason, they are not intended for use outside laboratory environments.
Final Thoughts
Research peptides are unlocking new frontiers in scientific discovery, offering valuable tools for studying complex biological systems. From metabolic research to regenerative medicine, peptides like BPC-157, CJC-1295, and Tirzepatide continue to advance our understanding of health, aging, and disease.
For those in scientific and academic fields, research peptides represent an exciting opportunity to explore innovative solutions and push the boundaries of what’s possible in medicine and biology.
Disclaimer: All products and information discussed in this article are intended strictly for research purposes. Research peptides are not for human consumption, therapeutic use, or diagnostic applications.