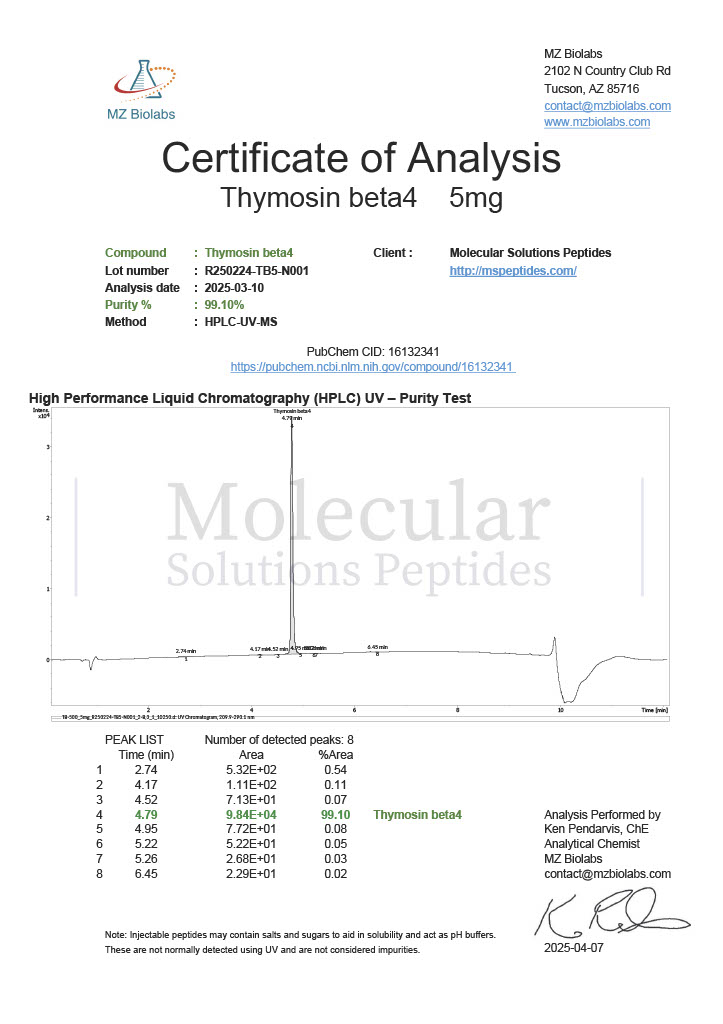
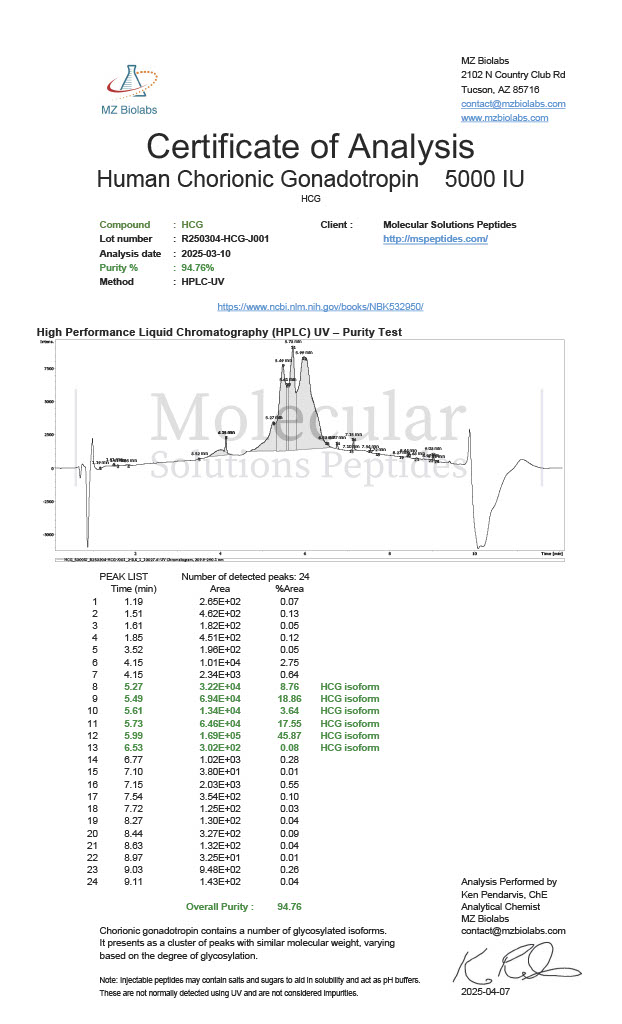
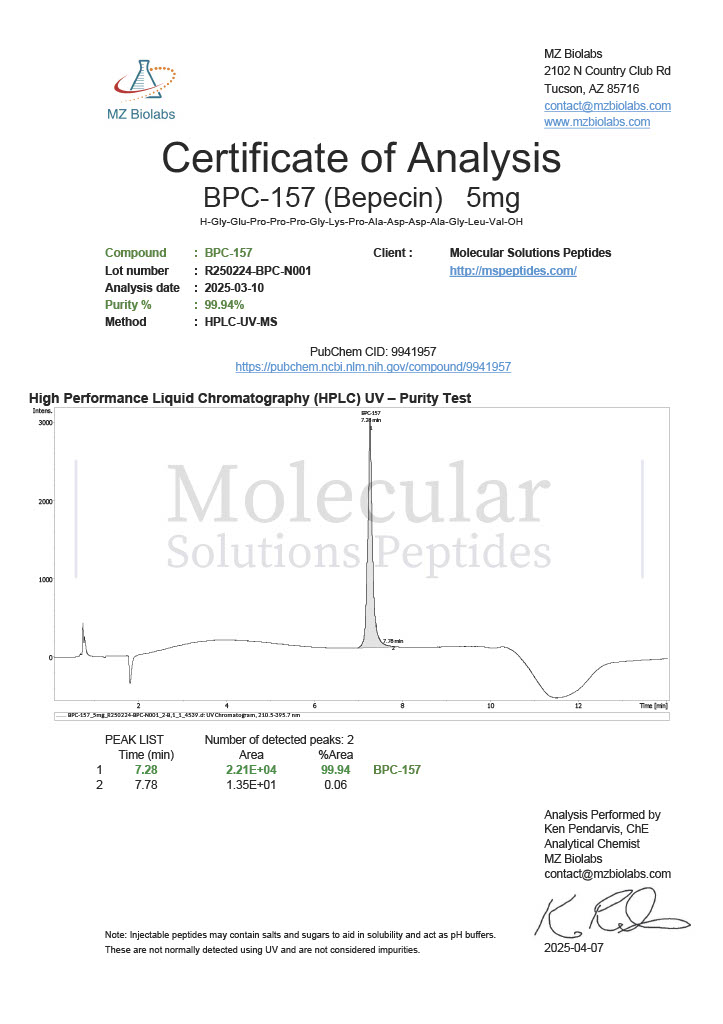
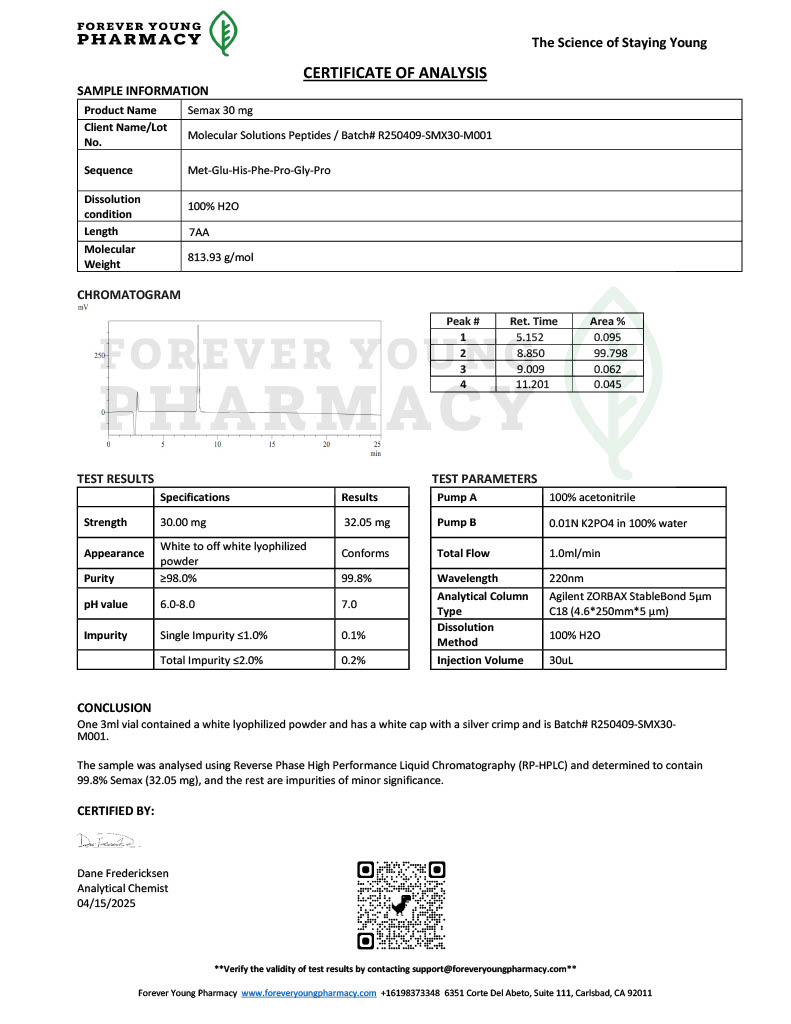
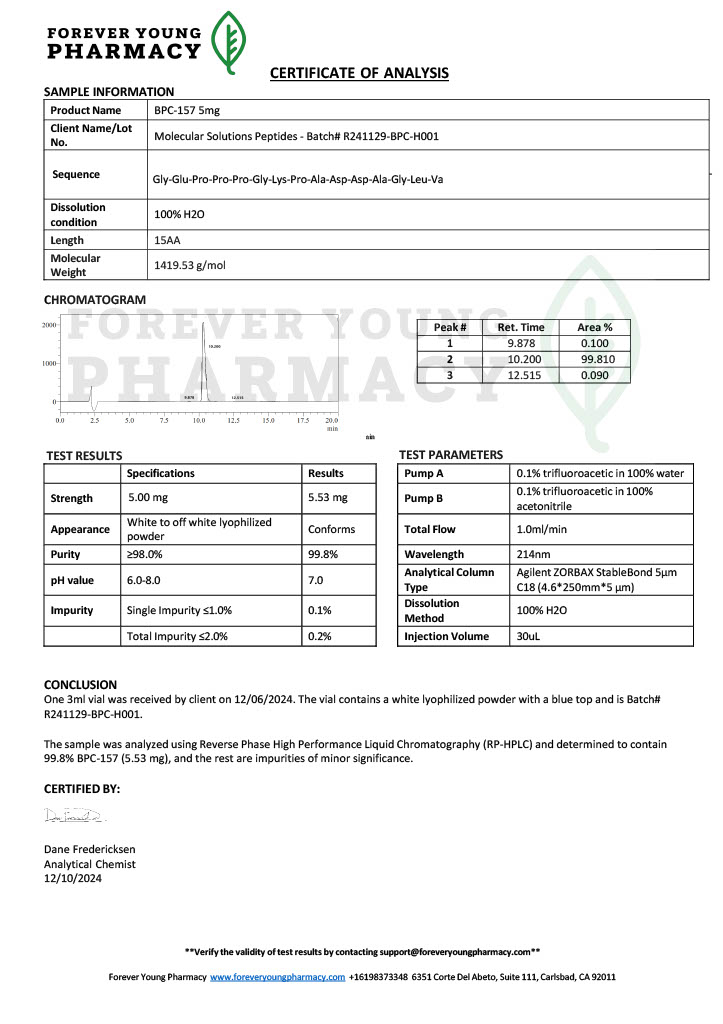
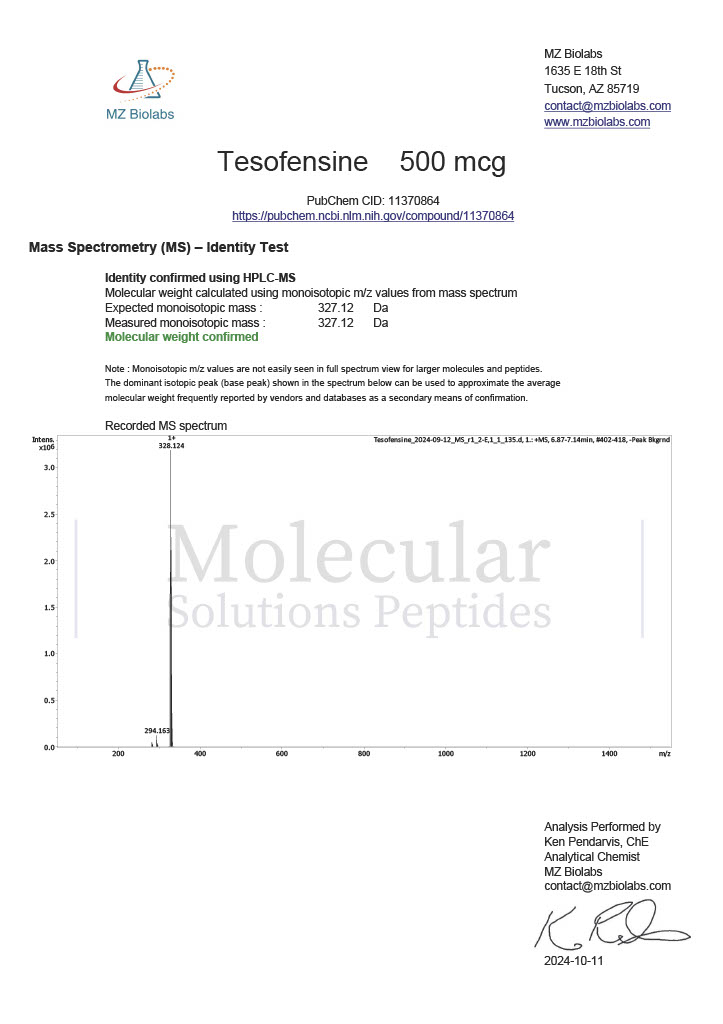
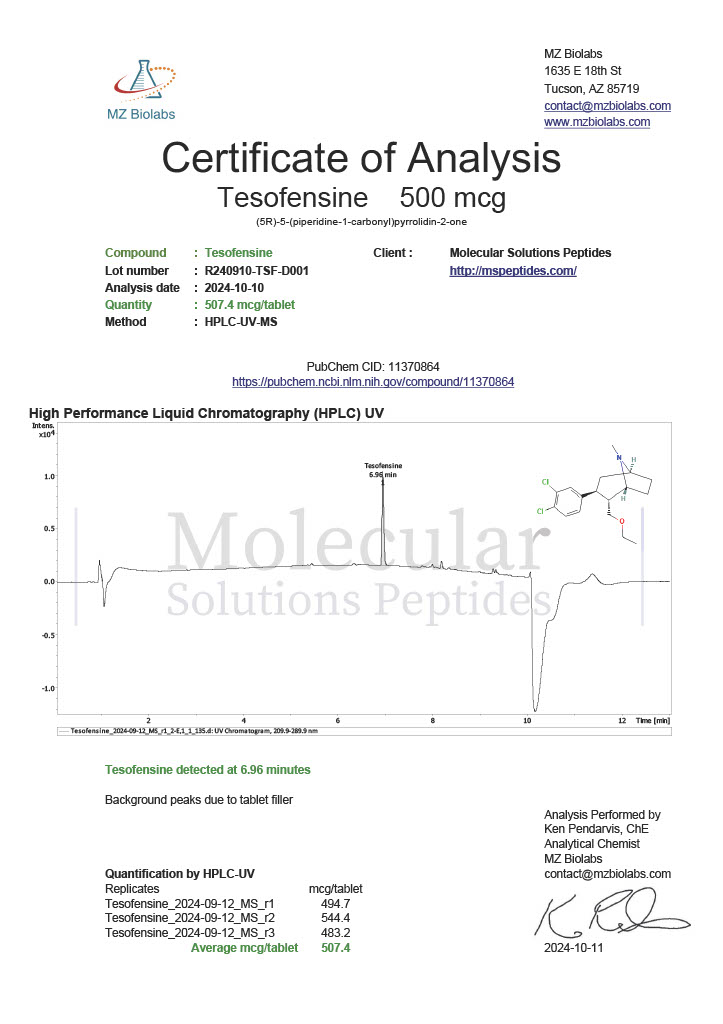
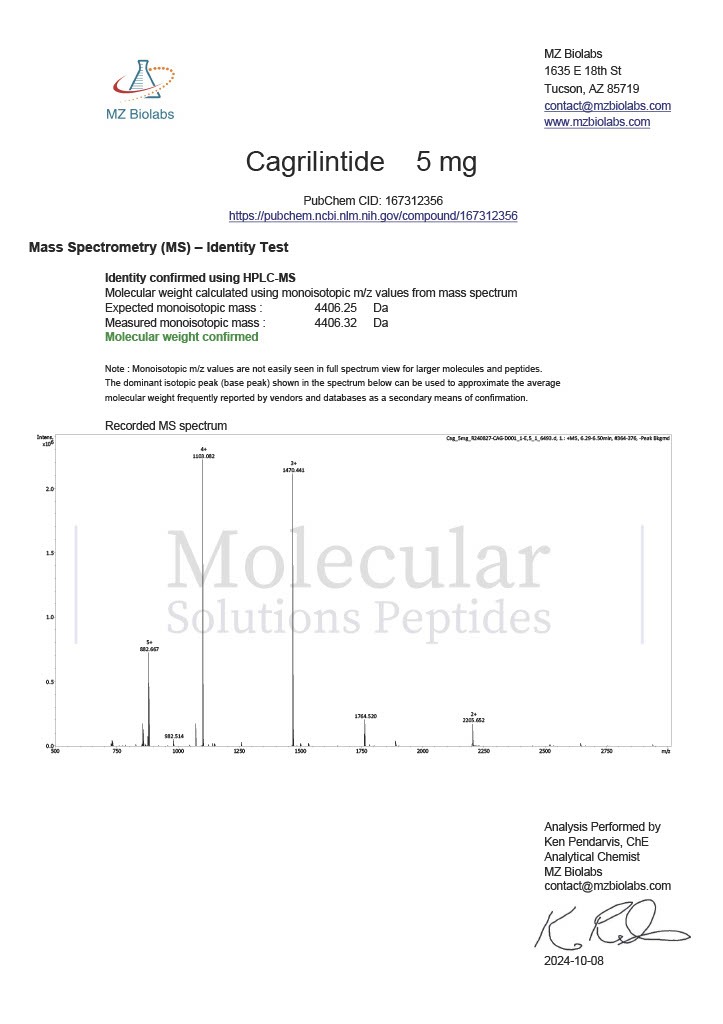
Cjc-1295 and Ipamorelin are synthetic peptides that have become widely referenced in laboratory and biochemical research focused on growth hormone regulation. When discussed together as Cjc-1295/Ipamorelin, the emphasis is not on a single compound but on a complementary research pairing that allows scientists to explore growth hormone release mechanisms in greater detail.
Introduction to Peptide Signaling Research
Peptides are short chains of amino acids that act as signaling molecules in many biological systems. In endocrine research, peptides that influence growth hormone release are studied to better understand how the pituitary gland responds to upstream signals. Growth hormone itself plays a role in a wide range of physiological processes, which makes the signaling pathways controlling its release a major area of interest in molecular biology.
Cjc-1295 and Ipamorelin were developed to target different receptors involved in growth hormone secretion. While each peptide can be studied independently, researchers often examine them together to evaluate how simultaneous receptor stimulation influences signaling patterns, amplitude, and duration.
What Is Cjc-1295?
Cjc-1295 is a synthetic analog of growth hormone releasing hormone, commonly abbreviated as GHRH. Native GHRH is produced in the hypothalamus and stimulates the anterior pituitary to release growth hormone. However, endogenous GHRH has a short half life, which limits its usefulness in controlled laboratory experiments.
From a research standpoint, Cjc-1295 serves as a tool to study prolonged GHRH receptor activation and downstream signaling cascades. Scientists can measure how sustained stimulation affects gene expression, hormone pulsatility, and feedback regulation within endocrine systems.
What Is Ipamorelin?
Ipamorelin is a synthetic peptide classified as a growth hormone secretagogue. Unlike Cjc-1295, which mimics GHRH, Ipamorelin acts primarily through the ghrelin receptor, also known as the growth hormone secretagogue receptor or GHS-R.
Ghrelin is a naturally occurring peptide that stimulates growth hormone release through a pathway distinct from GHRH. Ipamorelin was developed to selectively activate this receptor while minimizing interaction with other receptors that may influence unrelated hormonal systems. This selectivity makes Ipamorelin particularly useful in research models where controlled stimulation is required.
In laboratory studies, Ipamorelin allows researchers to observe how ghrelin receptor activation contributes to growth hormone signaling independent of hypothalamic GHRH input. This helps isolate variables and clarify the role of different receptor pathways.
Distinct Pathways, Complementary Functions
One of the primary reasons Cjc-1295 and Ipamorelin are studied together is that they activate separate but converging signaling pathways. Cjc-1295 stimulates the GHRH receptor, while Ipamorelin activates the ghrelin receptor. Both receptors ultimately influence the release of growth hormone from pituitary cells, but they do so through different intracellular mechanisms.
When these pathways are activated simultaneously in experimental models, researchers can evaluate whether the combined effect differs from stimulation of either pathway alone. This concept of synergistic signaling is central to many areas of molecular biology, as it reflects how complex biological systems integrate multiple inputs.
By studying Cjc-1295/Ipamorelin together, scientists can analyze receptor crosstalk, signal amplification, and the timing of downstream responses. These observations contribute to a more complete understanding of endocrine regulation at the cellular level.
Synergy in Experimental Design
Synergy in peptide research does not imply increased potency in a practical sense, but rather an opportunity to study interactions between signaling systems. In controlled experiments, researchers may observe differences in growth hormone pulse frequency, peak amplitude, or total output when both peptides are present compared to individual administration.
These findings help researchers answer key questions, such as whether GHRH and ghrelin pathways operate independently or influence each other through shared intracellular messengers. Data gathered from such studies can inform broader models of hormone regulation and feedback control.
Importantly, synergy in this context is a hypothesis tested under laboratory conditions. Outcomes depend on variables such as peptide concentration, exposure time, cell type, and experimental environment.
Molecular Structure and Stability Considerations
From a biochemical perspective, both Cjc-1295 and Ipamorelin are relatively small peptides, but their structural differences are significant. Cjc-1295 contains modifications that enhance stability and receptor affinity, while Ipamorelin is engineered for receptor selectivity and minimal off target interaction.
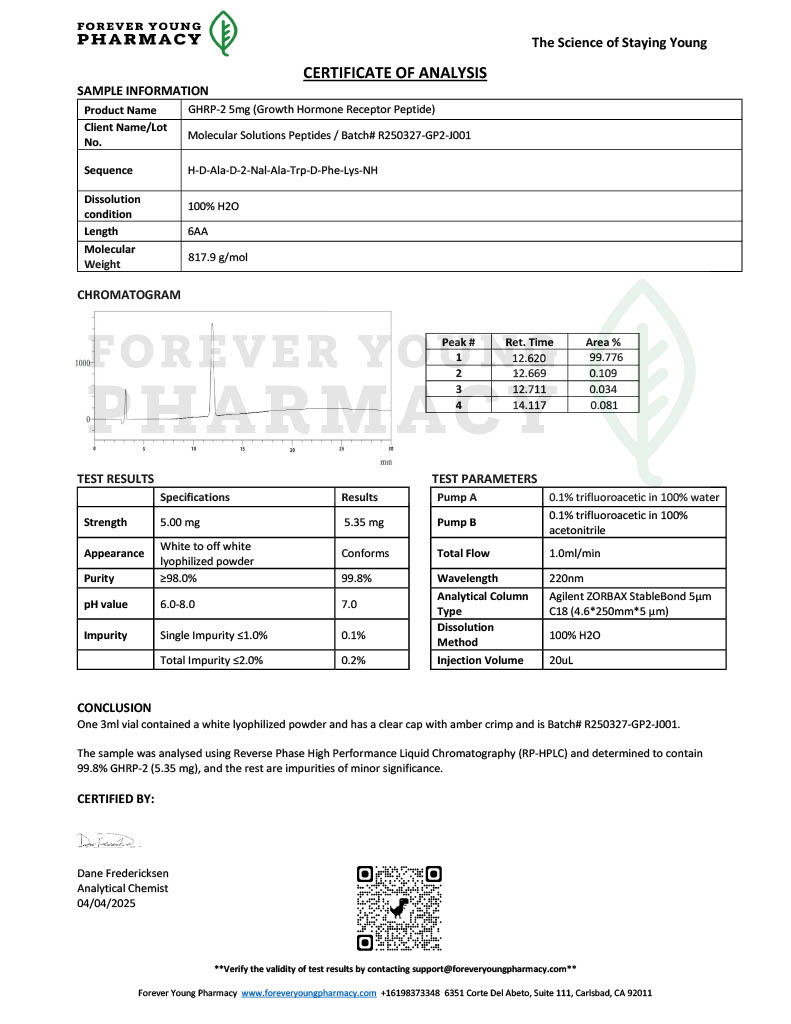
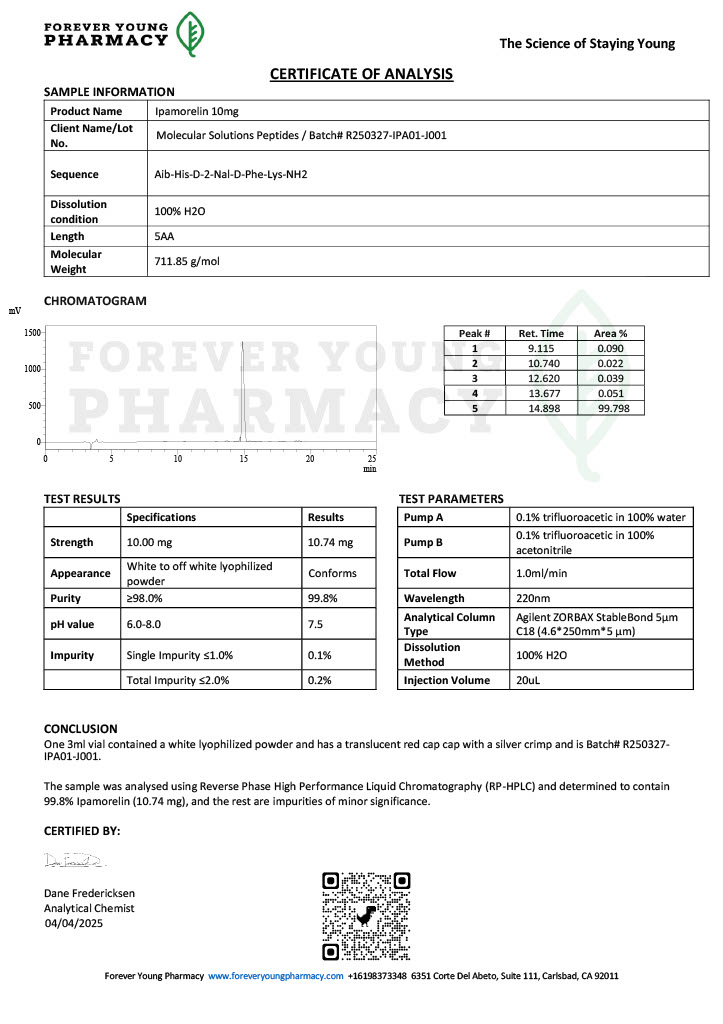
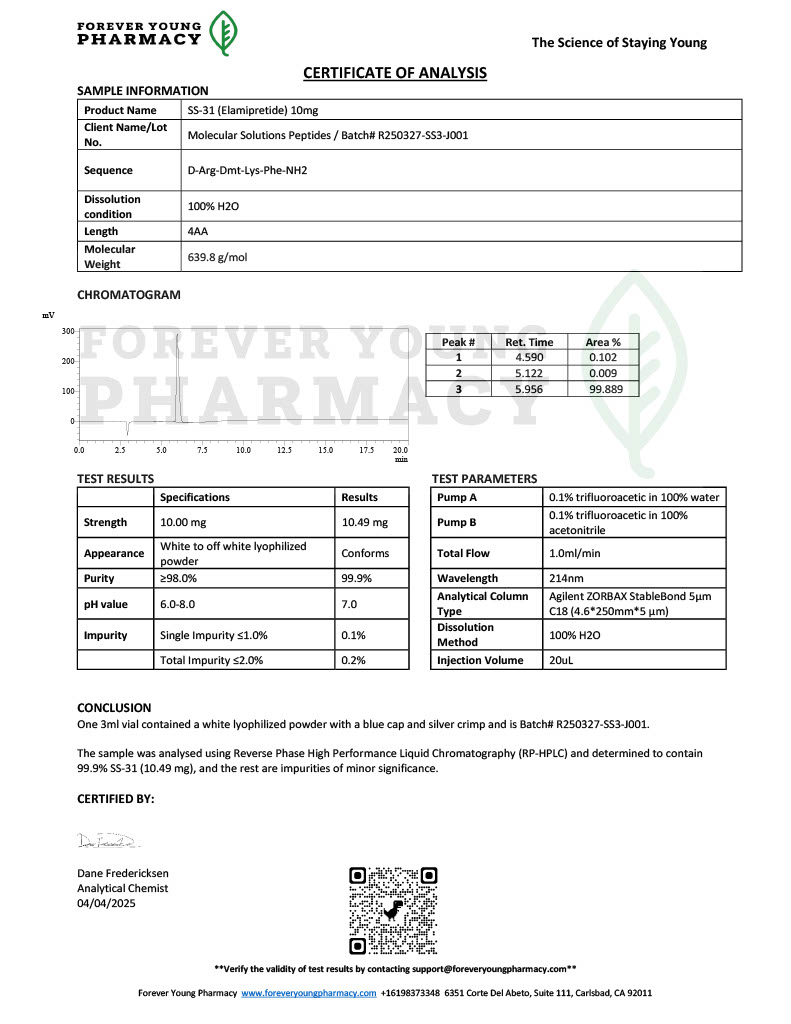
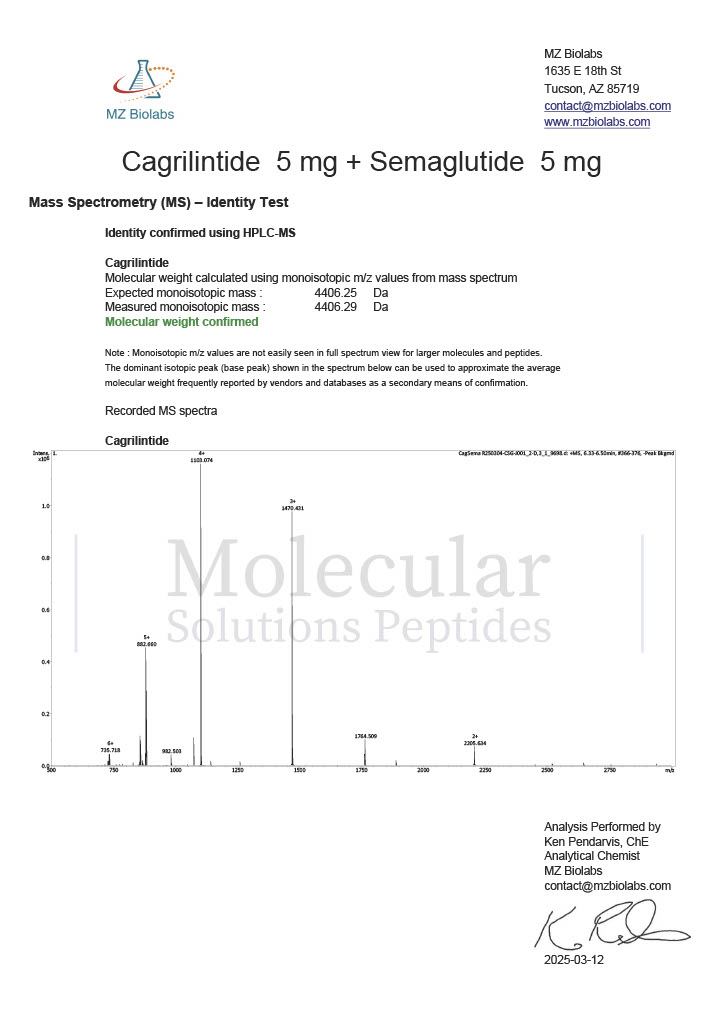
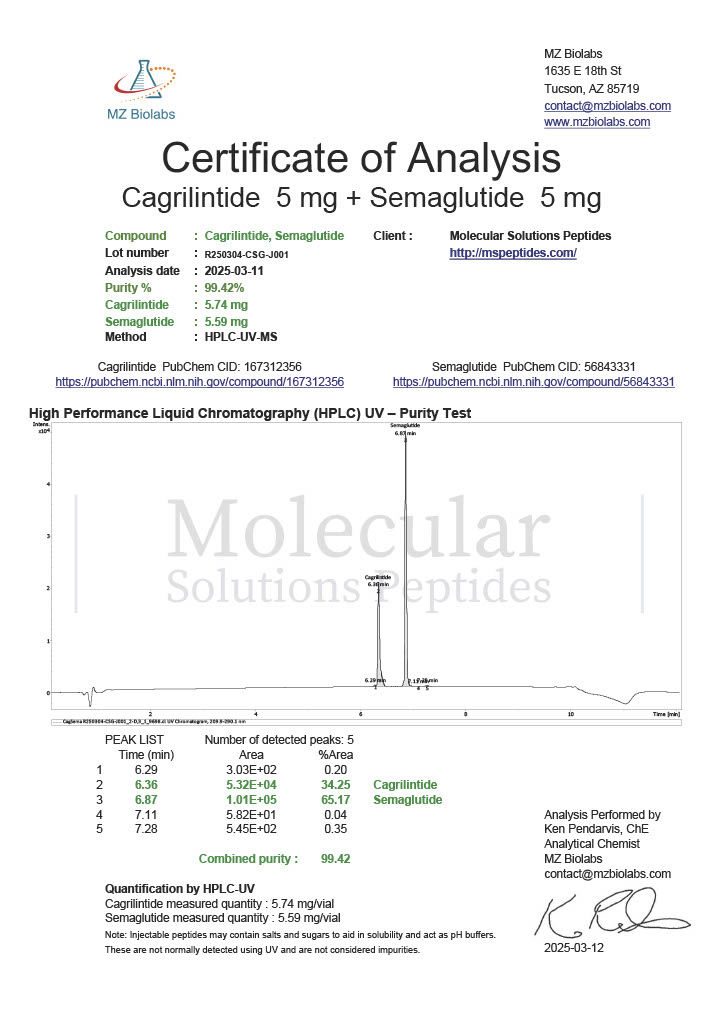
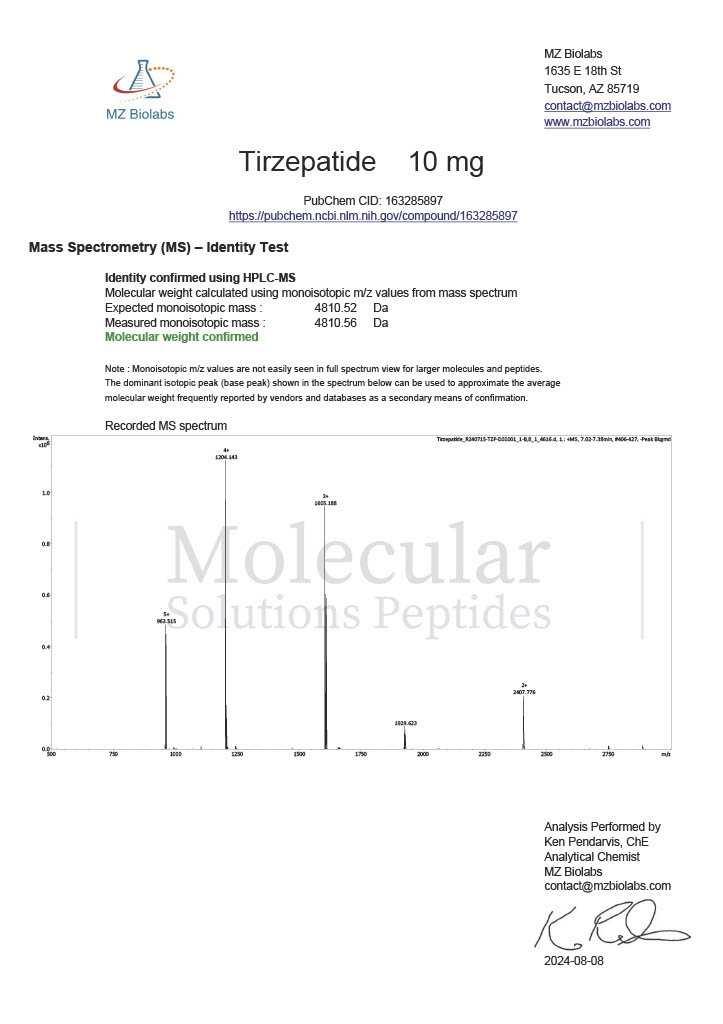
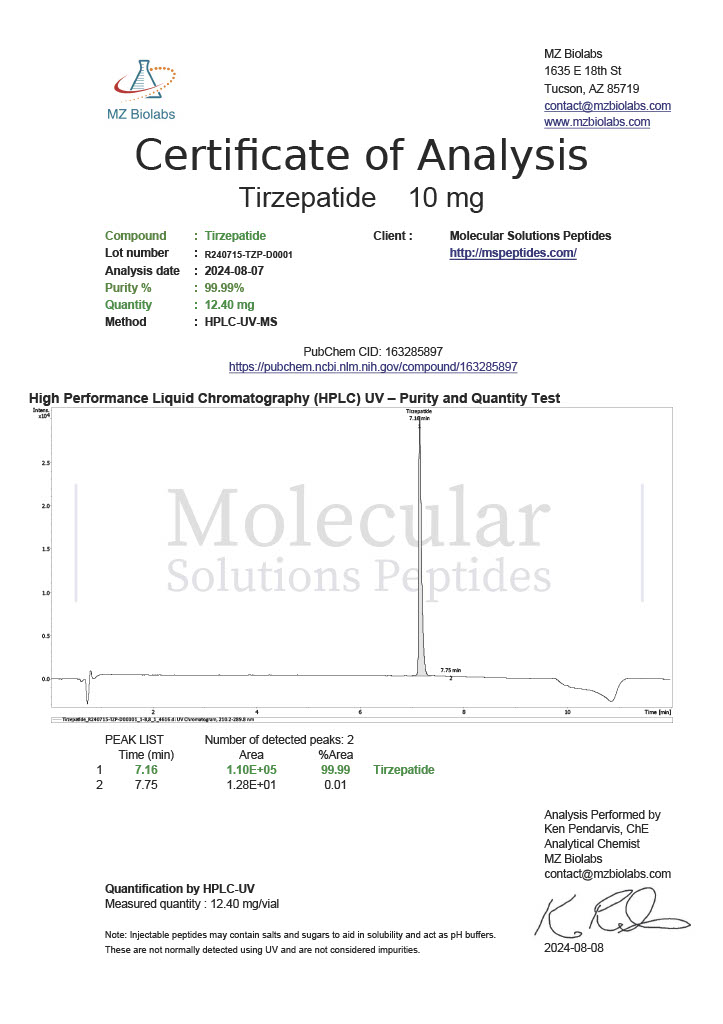
Stability is a critical factor in peptide research. Degradation can lead to inconsistent results or misinterpretation of data. As a result, researchers pay close attention to peptide purity, storage conditions, and reconstitution protocols. Analytical methods such as high performance liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry are commonly used to confirm peptide identity before experimental use.
Studying Cjc-1295/Ipamorelin together also requires careful consideration of their respective stability profiles. Differences in degradation rates may influence observed outcomes if not properly controlled.
Receptor Binding and Signal Transduction
At the cellular level, receptor binding initiates a cascade of intracellular events. GHRH receptor activation typically involves cyclic AMP signaling, while ghrelin receptor activation often engages phospholipase C pathways. Both ultimately influence transcription factors and gene expression related to growth hormone synthesis and release.
By analyzing these pathways in parallel, researchers can map how different second messengers interact or converge. This information is valuable beyond growth hormone research, as it provides insight into general principles of receptor signaling and cellular communication.
Cjc-1295/Ipamorelin research often includes measurements of intracellular signaling markers, receptor expression levels, and downstream hormone related genes. These data points help build a comprehensive picture of how peptide signals are processed by cells.
Importance of Controlled Research Contexts
It is essential to emphasize that Cjc-1295/Ipamorelin is studied within controlled laboratory environments. Variables such as temperature, pH, peptide concentration, and exposure duration are tightly regulated to ensure reproducibility and accuracy.
The goal of such research is not application, but understanding. Insights gained from peptide signaling studies can contribute to broader scientific knowledge, inform future hypotheses, and support the development of more refined experimental tools.
Cjc-1295/Ipamorelin represents a valuable pairing in peptide research because it allows scientists to explore how distinct growth hormone related pathways interact at the molecular and cellular levels. By stimulating both GHRH and ghrelin receptors, researchers can examine synergy, receptor crosstalk, and downstream signaling in a controlled and measurable way.
As peptide research continues to evolve, combinations like Cjc-1295/Ipamorelin will continue to be studied for their ability to reveal complex biological interactions that cannot be observed through single pathway studies alone.
Disclaimer: All products on this site are for Research, Development use only. Products are Not for Human use of any kind. The statements made within this website have not been evaluated by the US Food and Drug Administration. The statements and the products of this company are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.